Thermo Scientific™ OXSAS™ X-Ray Fluorescence Analytical Software
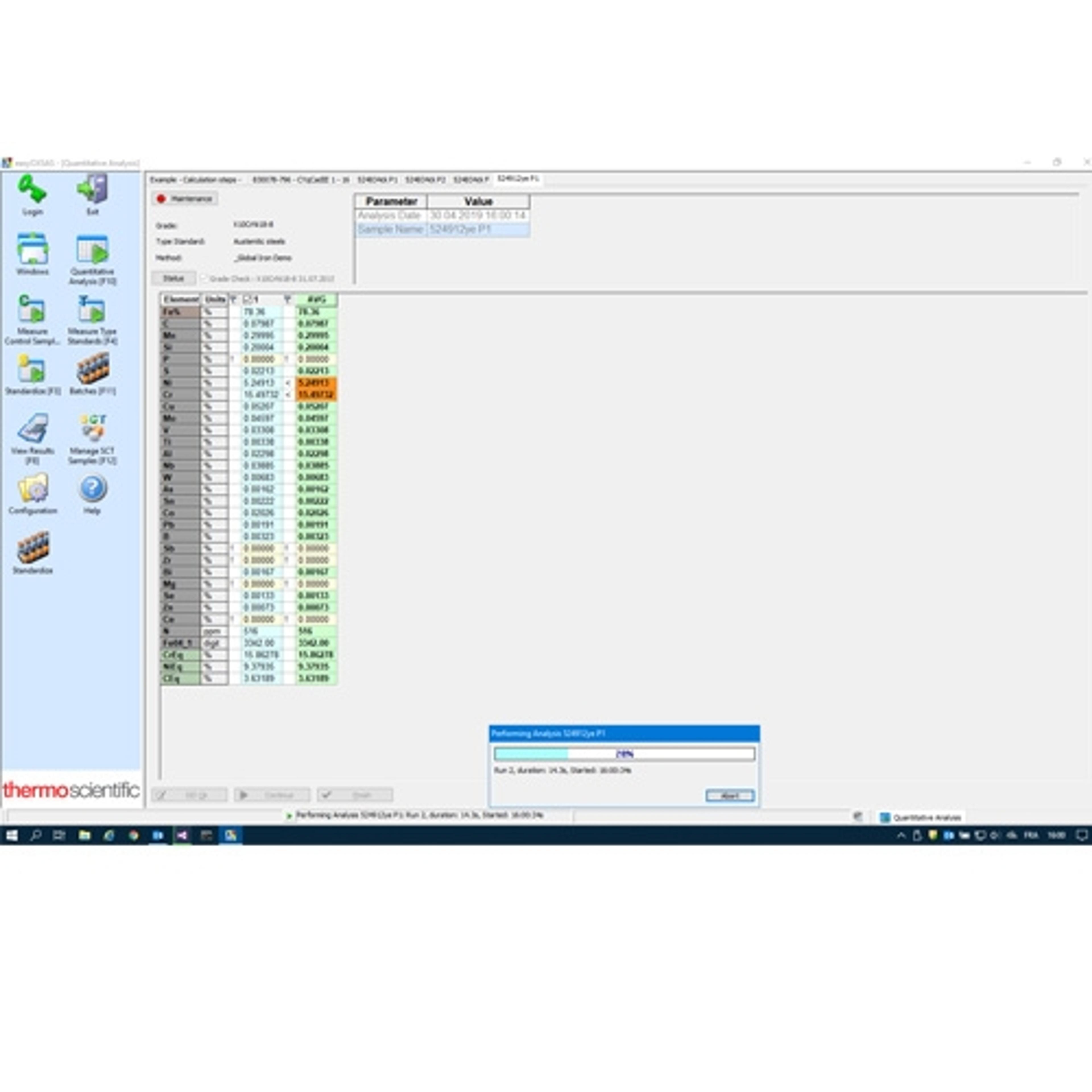
Thermo Fisher ScientificEnhance your lab efficiency and productivity with a customizable software solution that operates with XRF spectrometers. Flexible and powerful OXSAS X-ray Fluorescence Analytical Software performs rapid, high-quality sample analysis using template-driven operations. Optional standardless quantitative analysis packages offer additional versatility for all laboratories that analyze a wide range of materials.