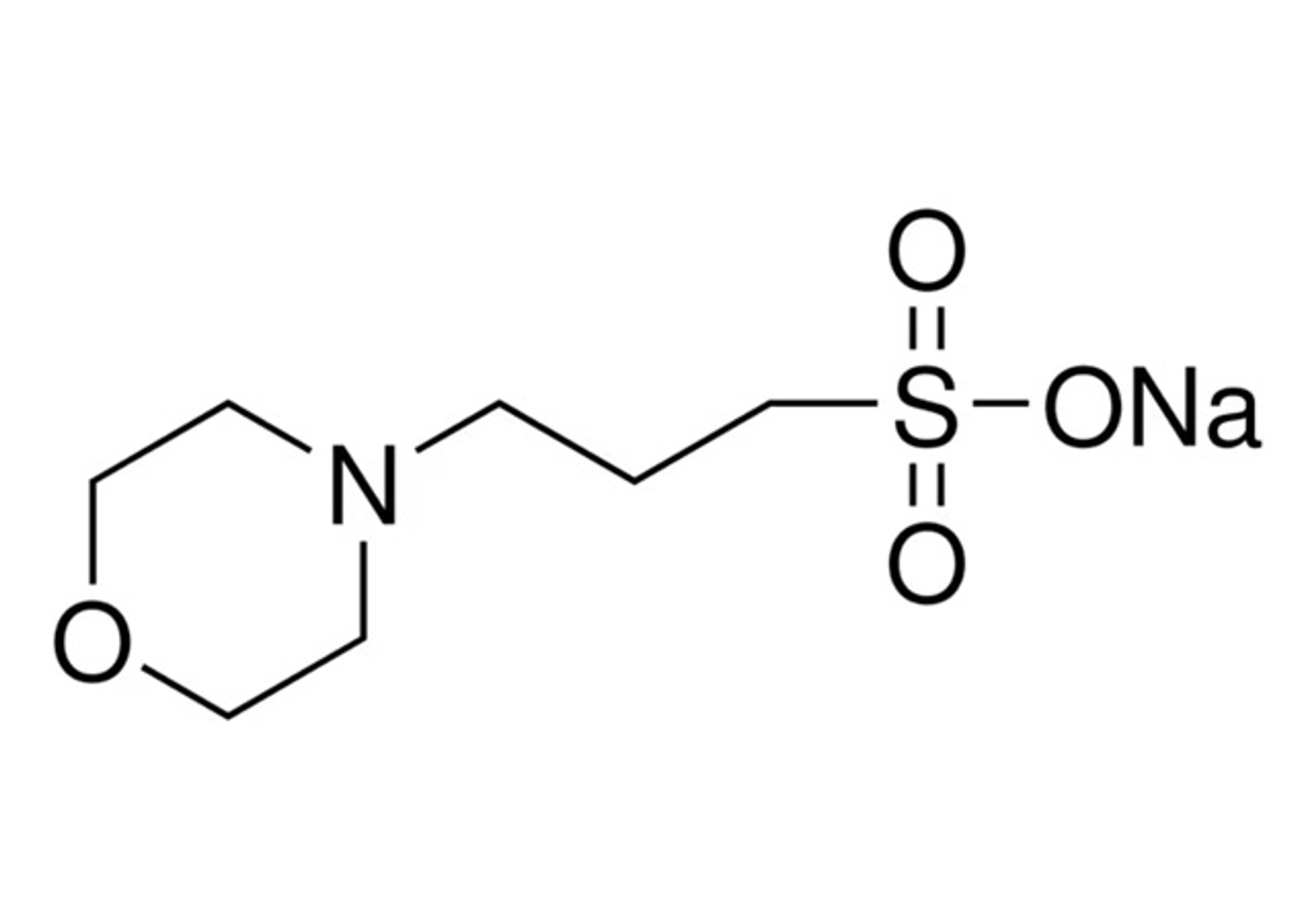
HEPES
BioPerformance Certified, ≥99.5% (titration), suitable for cell culture
HEPES buffer does not confer cytotoxic effects on cells and thus can be used in animal cell cultures.
HEPES has been described as one of the best all-purpose buffers available for biological research. At biological pH, the molecule is zwitterionic, and is effective as a buffer at pH 6.8 to 8.2. HEPES has been used in a wide variety of applications, including tissue culture. It is commonly used to buffer cell culture media in air. HEPES finds its usage in in vitro experiments on Mg.
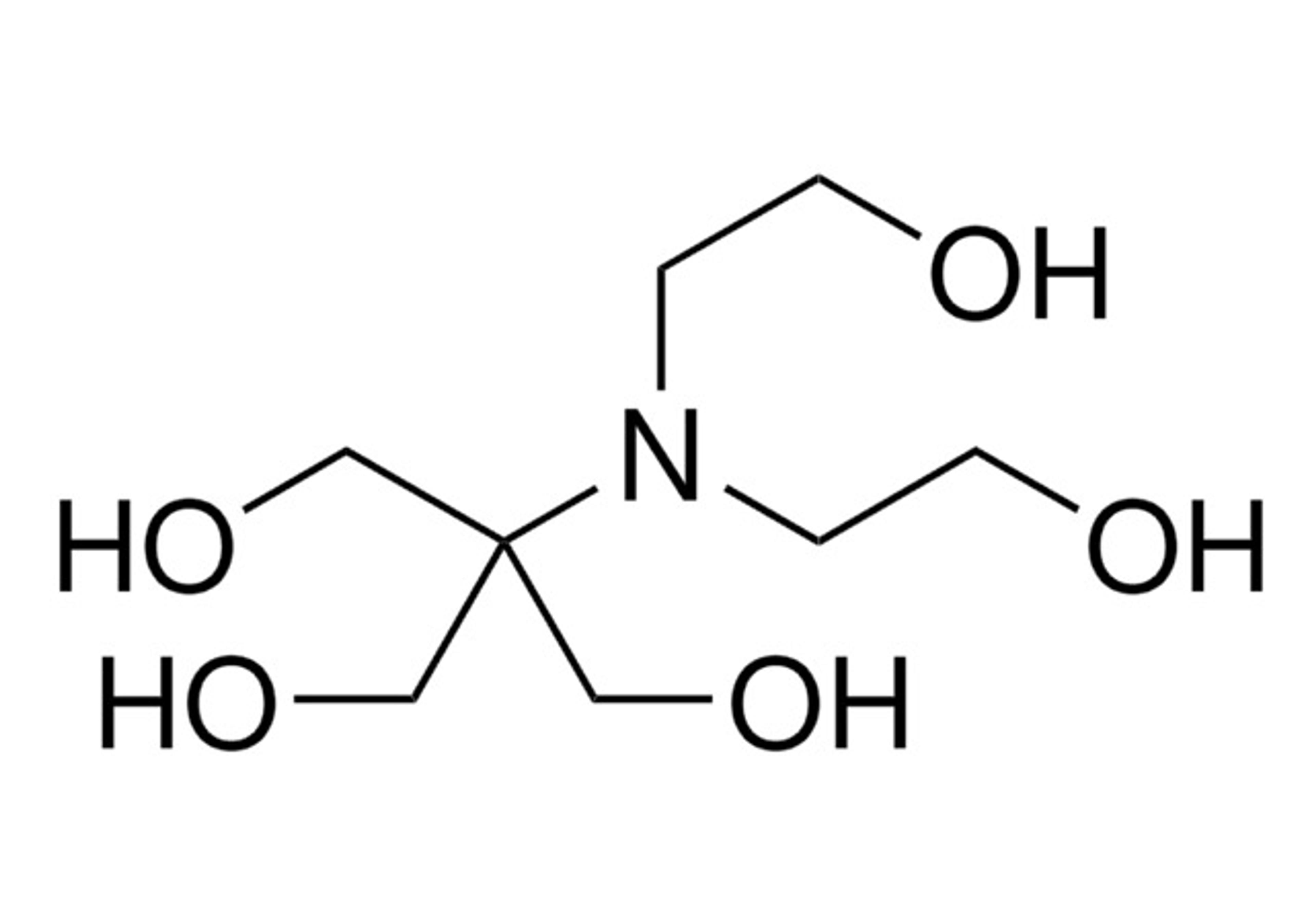
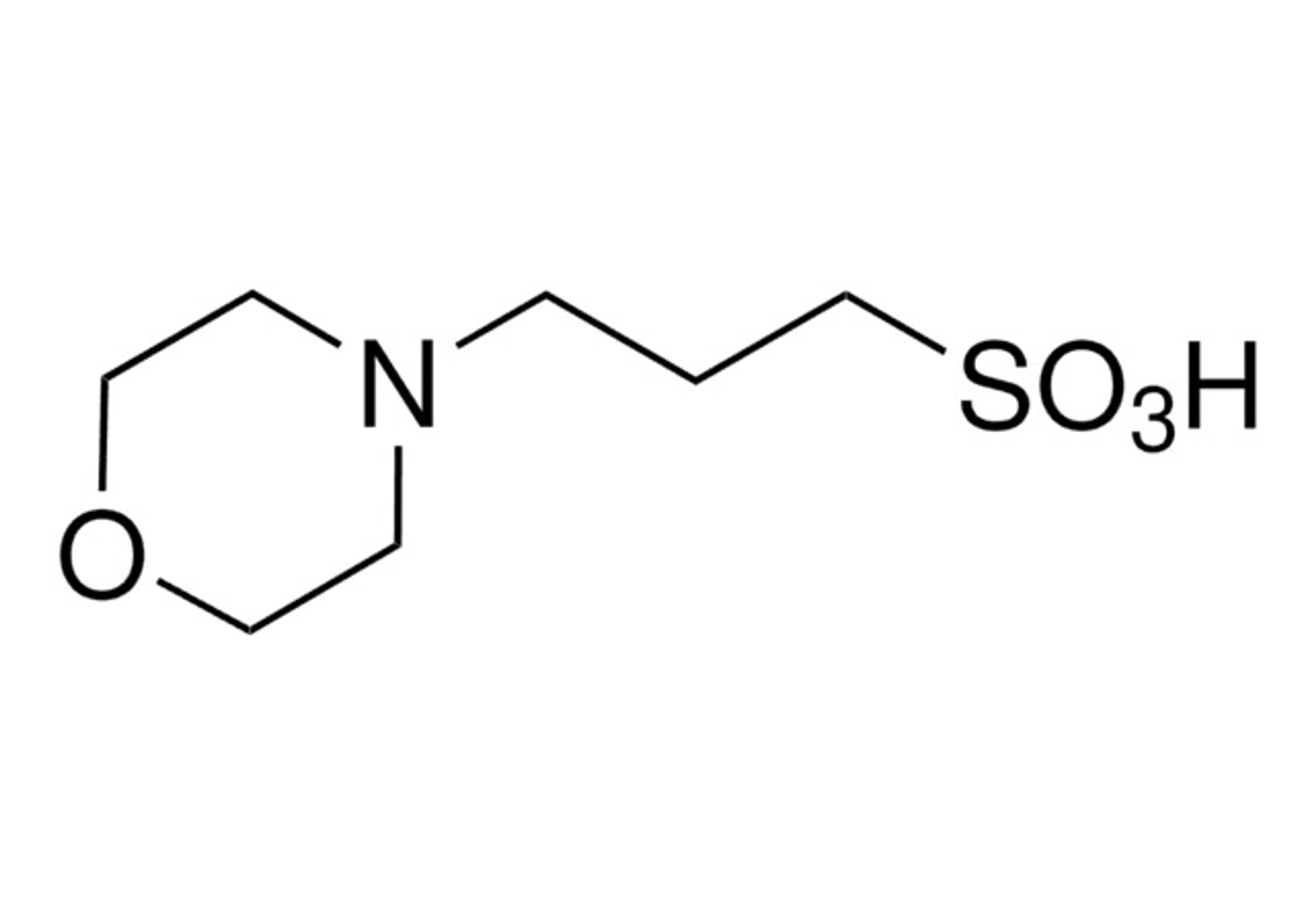
HEPES, or 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)piperazine-1-ethane-sulfonic acid, is a zwitterionic N-substituted aminosulfonic acid buffer. It demonstrates outstanding buffering capacity in the pH range of 6.8 to 8.2, boasting a pKa of 7.48 at 25°C. Widely acknowledged as one of the most versatile buffers, HEPES is extensively utilized in cell biology, biochemical, and biological research. A notable attribute is its non-reactivity with metal ions. Unlike many buffers, HEPES does not form significant complexes with most metals, making it suitable for applications involving metal ions without affecting their activity. This characteristic enhances its utility as a ""non-coordinating buffer."" In cell culture, HEPES excels in maintaining a stable physiological pH, even amidst fluctuations in carbon dioxide concentration resulting from cellular respiration. This sets it apart from bicarbonate buffers (NaHCO3), which, though commonly used, are less effective in pH stability.
HEPES also proves advantageous in various biological and biochemical processes. Its ampholytic nature makes it suitable as a separator for creating pH gradients in isoelectric focusing, a technique often employed in protein separation and analysis. Moreover, HEPES exhibits minimal interference with DNA-restriction enzyme reactions compared to buffers with fewer substituted amine groups, such as Tris. This makes it a preferred choice for applications involving DNA manipulation and analysis. Beyond these specific applications, HEPES is valuable in numerous other biological and biochemical processes, including immunoprecipitation, cell lysis, and live cell imaging. Its versatility, coupled with exceptional pH buffering capacity and minimal interaction with other molecules, establishes HEPES as an indispensable tool across diverse research domains.