Blood sample donation accelerates Actiphage TB study
The University of California San Diego has donated over 2,000 previously obtained frozen PBMC samples
10 Apr 2024
PBD Biotech
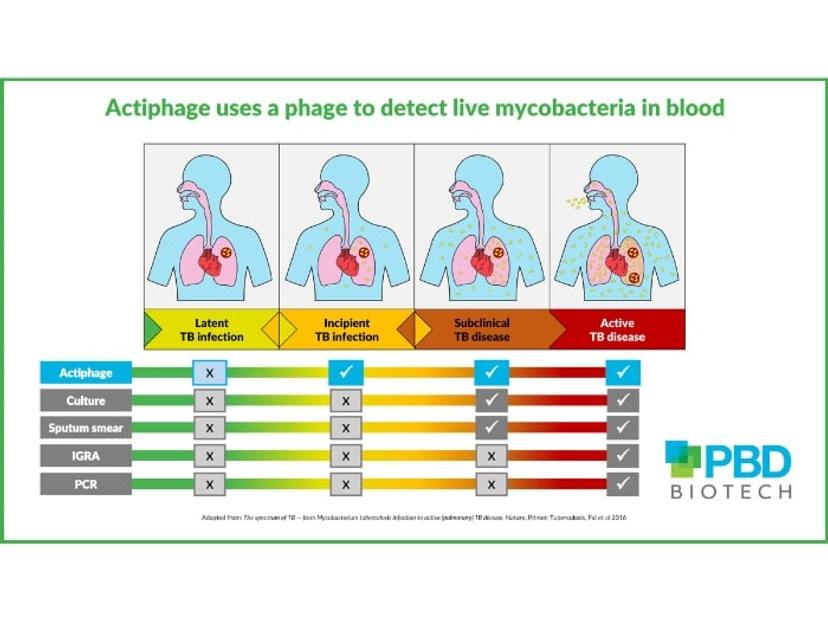
New research reveals that Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the pathogen that causes tuberculosis, can conceal itself within peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) to evade detection from the body’s immune system. This knowledge, gained from studies with the phage-based diagnostic Actiphage TB, provides new insights into disease progression. The University of California San Diego (UC San Diego) has donated over 2,000 previously obtained frozen PBMC samples to accelerate development of this promising diagnostic.
Jane Theaker, CEO of PBD Biotech, developers of the Actiphage TB blood test, says this support is invaluable. “Mycobacteria have tough walls and are incredibly resilient and difficult to culture. Phages are the natural enemy of bacteria and provide a mechanism for selectively detecting them in a blood sample, however preparing the samples is far from trivial. Our knowledge has so far been gained from fresh whole blood samples; having access to prepared and frozen PBMC reduces the need to recruit more participants and offers another dimension to the study.”
Dr Timothy Rodwell, a Professor at UC San Diego, and a Senior Scientific Advisor at FIND, Switzerland has a particular interest in evaluating novel biomarkers for rapid diagnosis of TB. After evaluating the technology, he said, “There is an urgent need for a diagnostic that can detect those that are at risk of disease progression. We had this set of samples left over from a previous study that were collected, prepared, and stored according to a rigorous protocol. The samples are from those with known infection and their household contacts, so ideal for repurposing in a trial of Actiphage.”
